I will demonstrate how to establish a point to site connection in Azure, and connect from a Windows workstation to a virtual machine via its private IP address. Azure Point to Site Connection is part of the AZ-303 exam for becoming an Azure Solution Architect.
 Watch Azure Point to Site Connection in preparation for the AZ-303 exam
Watch Azure Point to Site Connection in preparation for the AZ-303 exam
Sometimes we need to have our workload running on a virtual machine with no public IP address. At the same time we want to connect to it from our workstation. In the picture below I created already a Windows 10 Client workstation in the West Europe region. In the Central US region I created a virtual network with another vm, Windows Server 2016 Datacenter. I did not assign a public IP address to it, so it has only a private IP address. I also installed the Internet Information Server (IIS) on it. Right now it’s only accessible from localhost and within this virtual network.
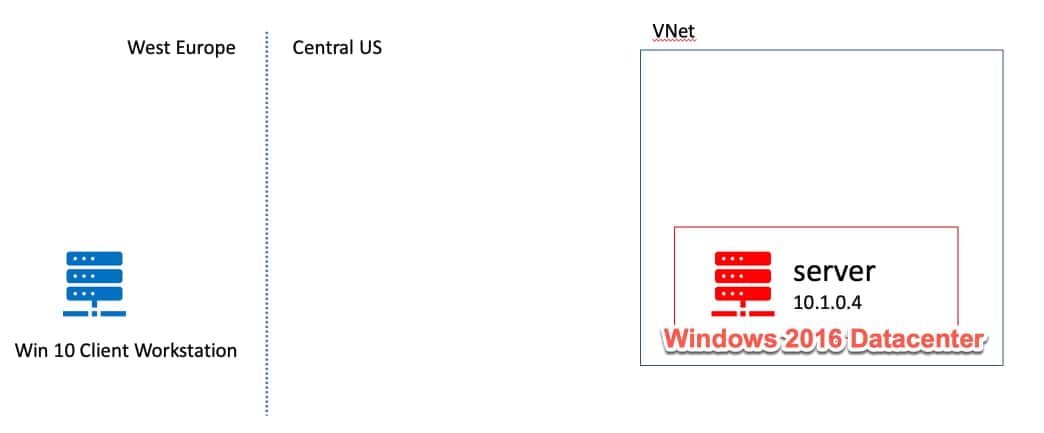 Pre-provisioned Azure resources
Pre-provisioned Azure resources
Our goal is to create what’s described below.
- Create a subnet gateway. The name
SubnetGatewayis important as it will be recognized as such of the virtual network gateway in the next step. - Create the virtual network gateway.
- Generate the root certificate and client certificate.
- Setup the point to site connection with the root certificate.
- Establish a connection from the client workstation to the server.
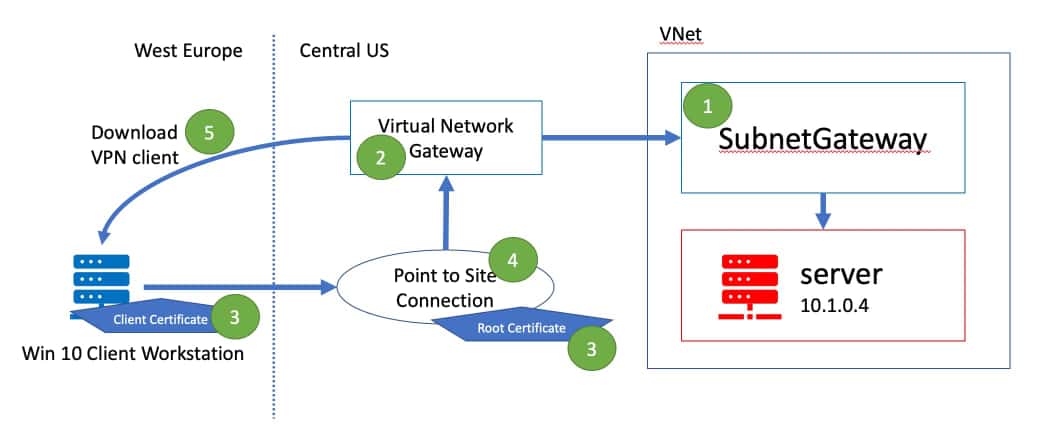 Architecture for point to site VPN connection
Architecture for point to site VPN connection
We start by adding the subnet gateway. You find it under Subnets within your VNet. The name GatewaySubnet is important, and you can’t change it. I leave the address range as it but feel free to give it a smaller range i.e. /27.
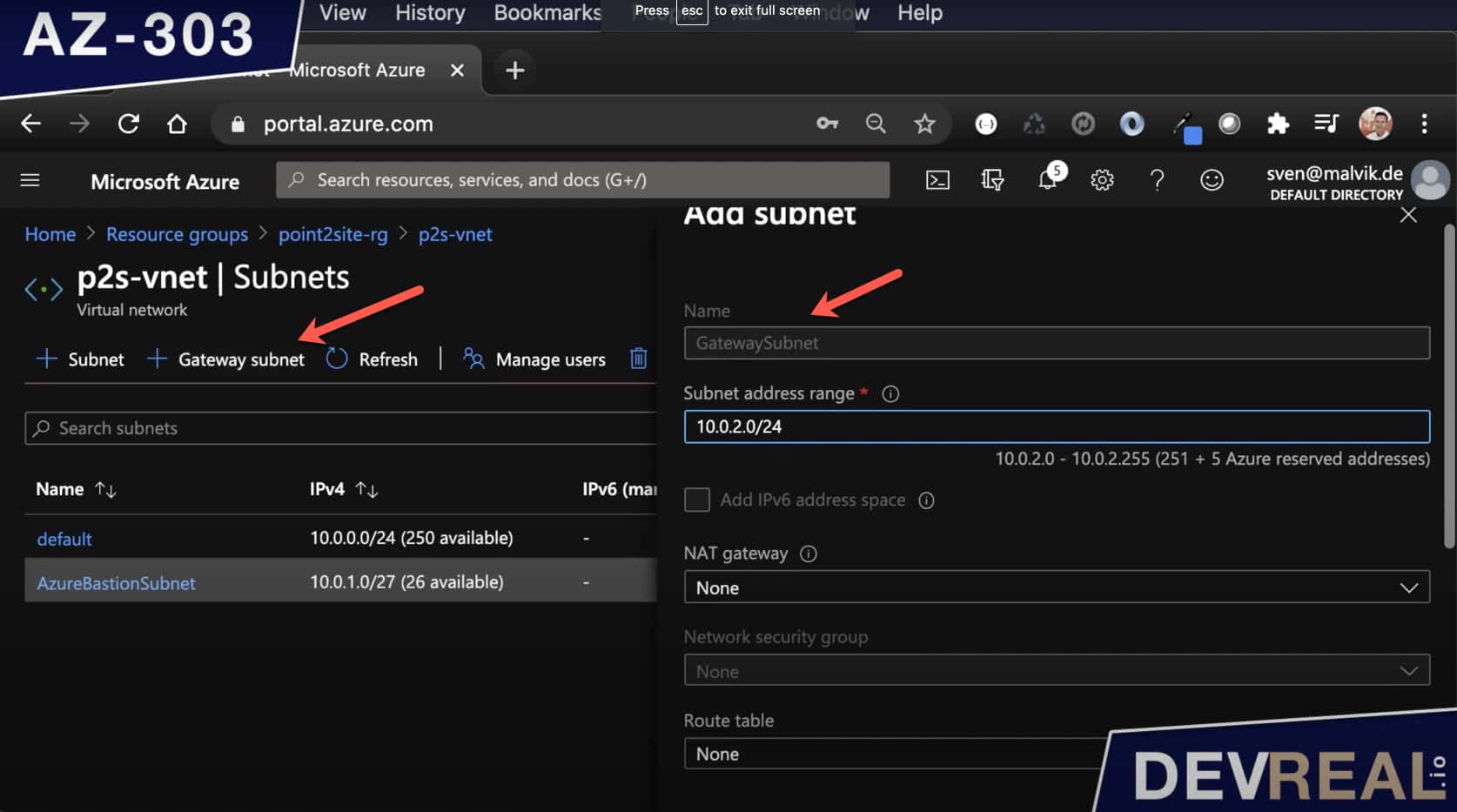 Creating Subnet Gateway
Creating Subnet Gateway
Now that we have the subnet gateway in place, we can create a virtual network gateway.
 Create Virtual Network Gateway
Create Virtual Network Gateway
We set the gateway type as VPN, and the VPN type as Route-based. The subnet is set automatically to your subnet gateway. That’s why the name is important.
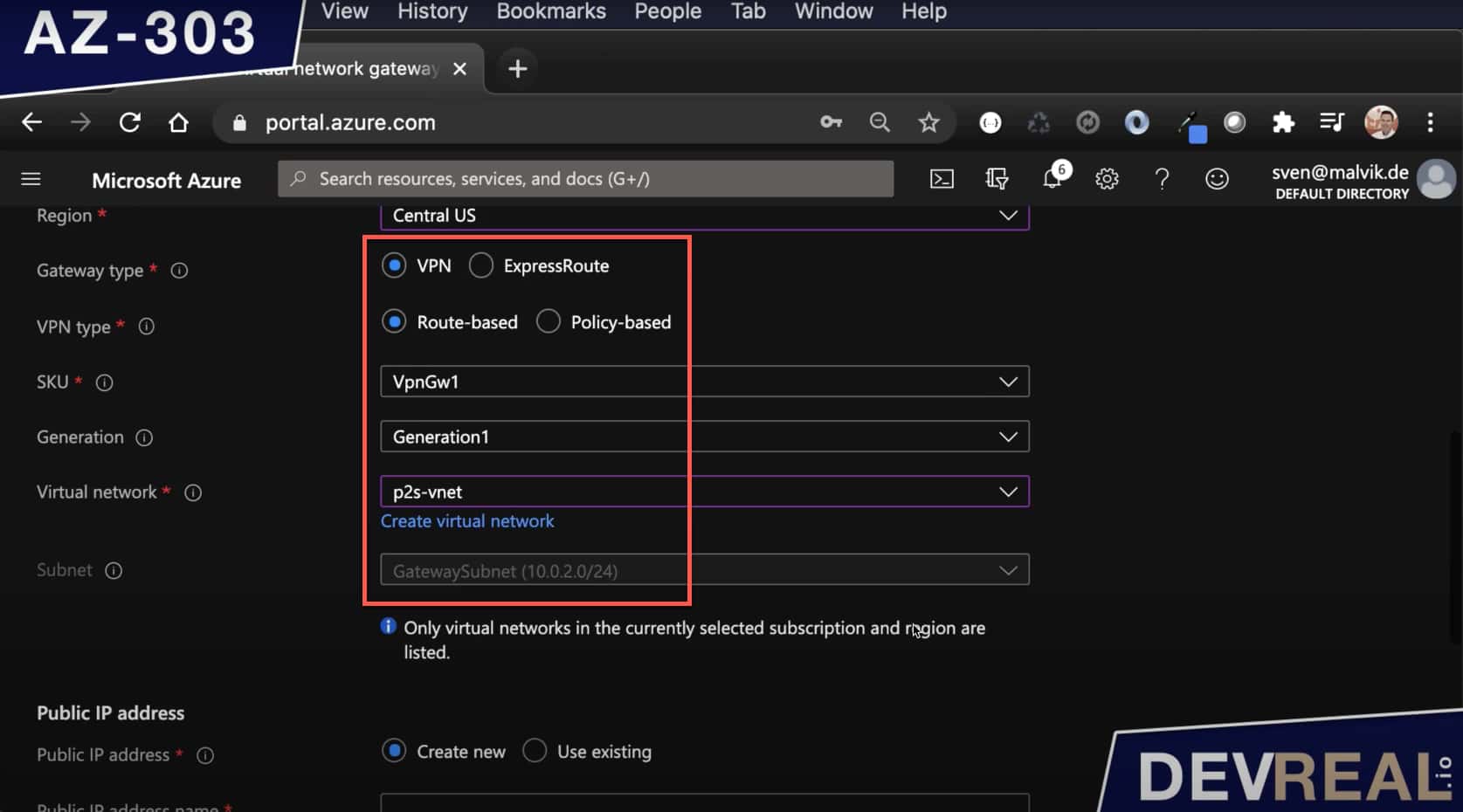 Azure Virtual Network Configuration
Azure Virtual Network Configuration
If we scroll down a bit a must not forget to name a public IP address that we need for establishing a VPN connection. We won’t use it directly for accessing the IIS.
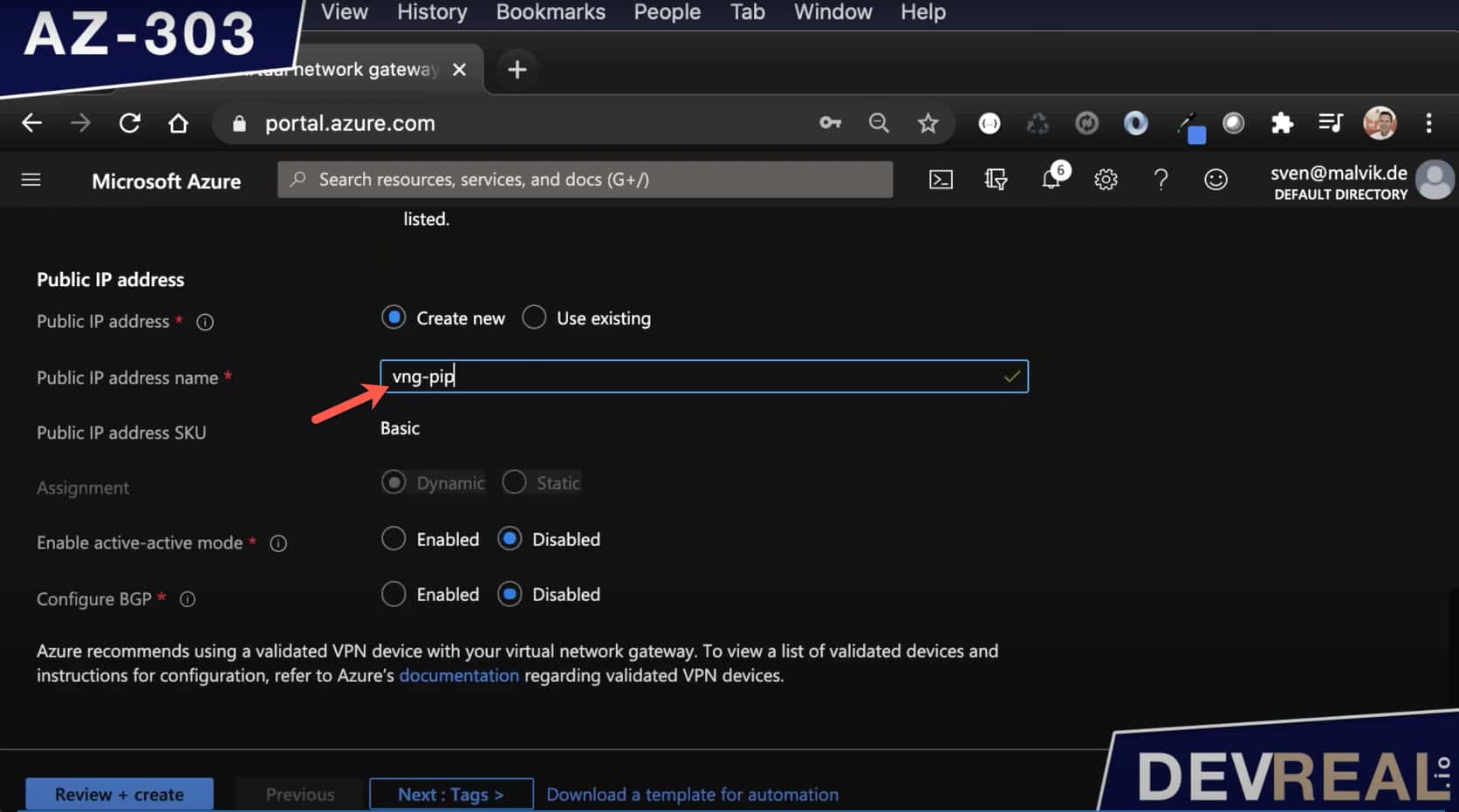 Azure Virtual Network Configuration Public IP address
Azure Virtual Network Configuration Public IP address
Now we need to create some certificates. First we need a root certificate. Your organization may already have one. Out of this root certificate, we create a client certificate that we need to have on the workstation.
First, login to the client workstation and open Powershell. Run the first command for the root certificate.
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -KeySpec Signature -Subject "CN=RootCertificate" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable -HashAlgorithm sha256 -KeyLength 2048 -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" -KeyUsageProperty Sign -KeyUsage CertSign
Then run the following command for creating the client certificate out of the root certificate.
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -DnsName P2SChildCert -KeySpec Signature -Subject "CN=ClientCertificate" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable -HashAlgorithm sha256 -KeyLength 2048 -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" -Signer $cert
You can see the result below.
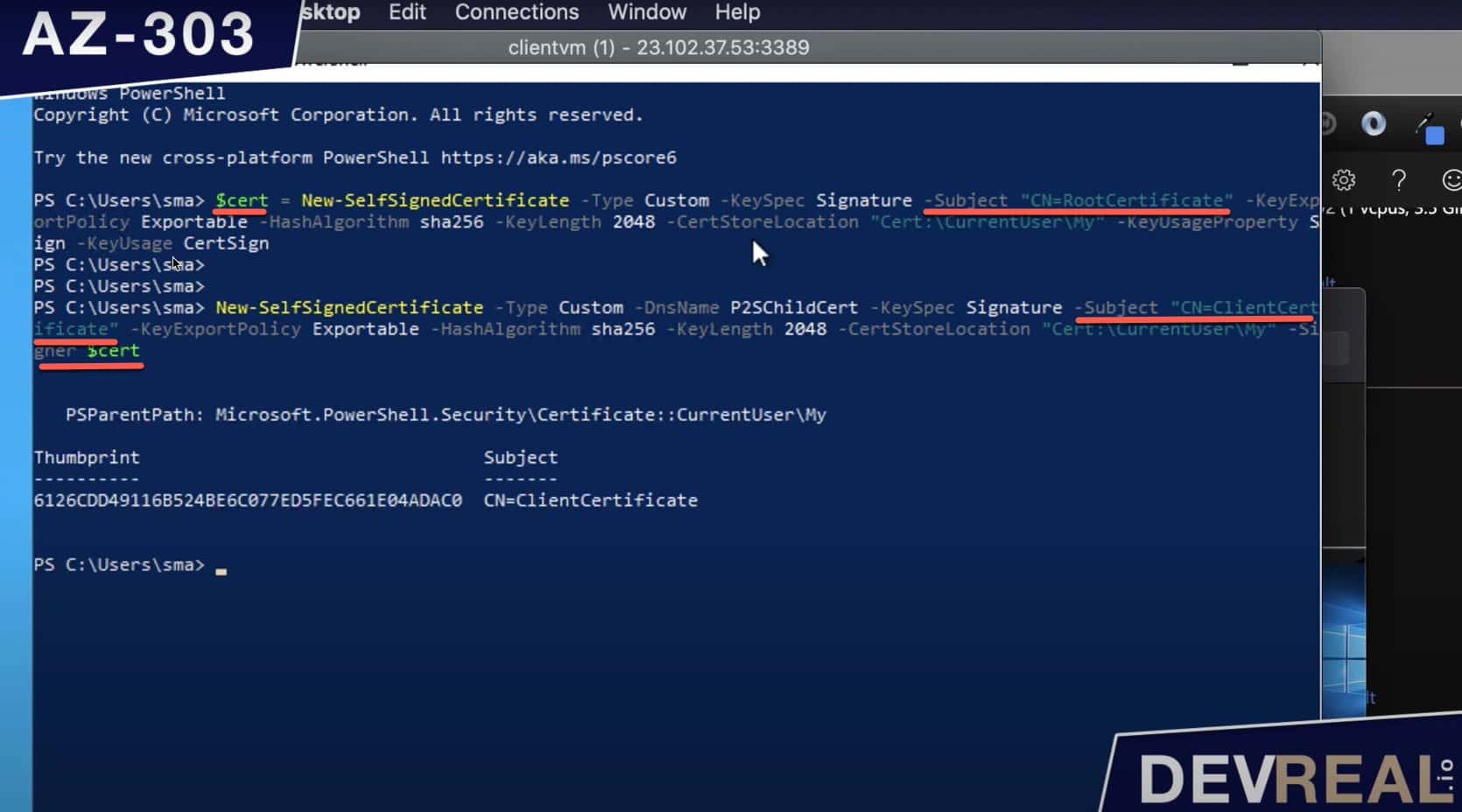 Creating self-signed certificates with PowerShell
Creating self-signed certificates with PowerShell
Search now for rootcert and right-click on it to open it with Notepad or any other text editor.
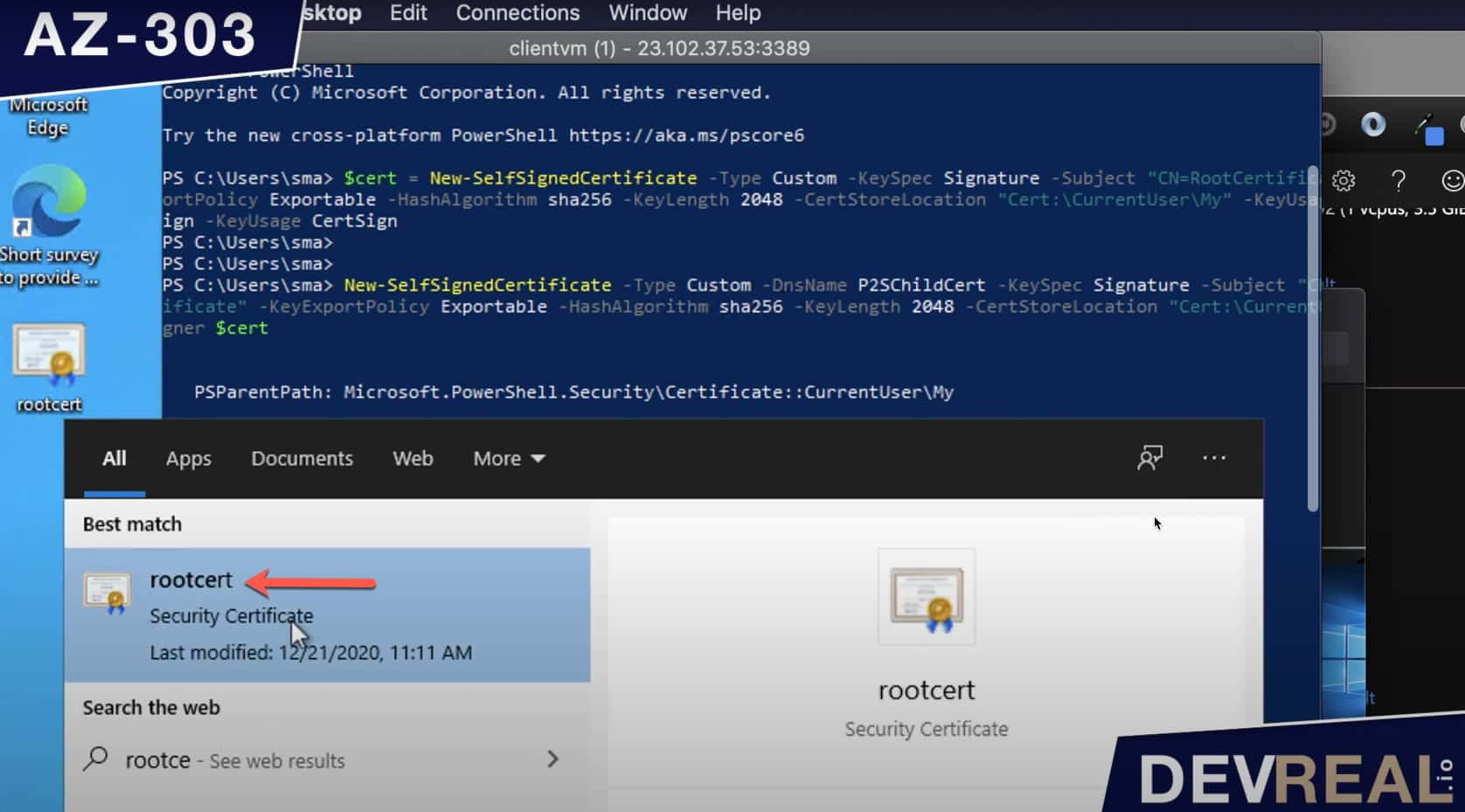 Search for rootcert
Search for rootcert
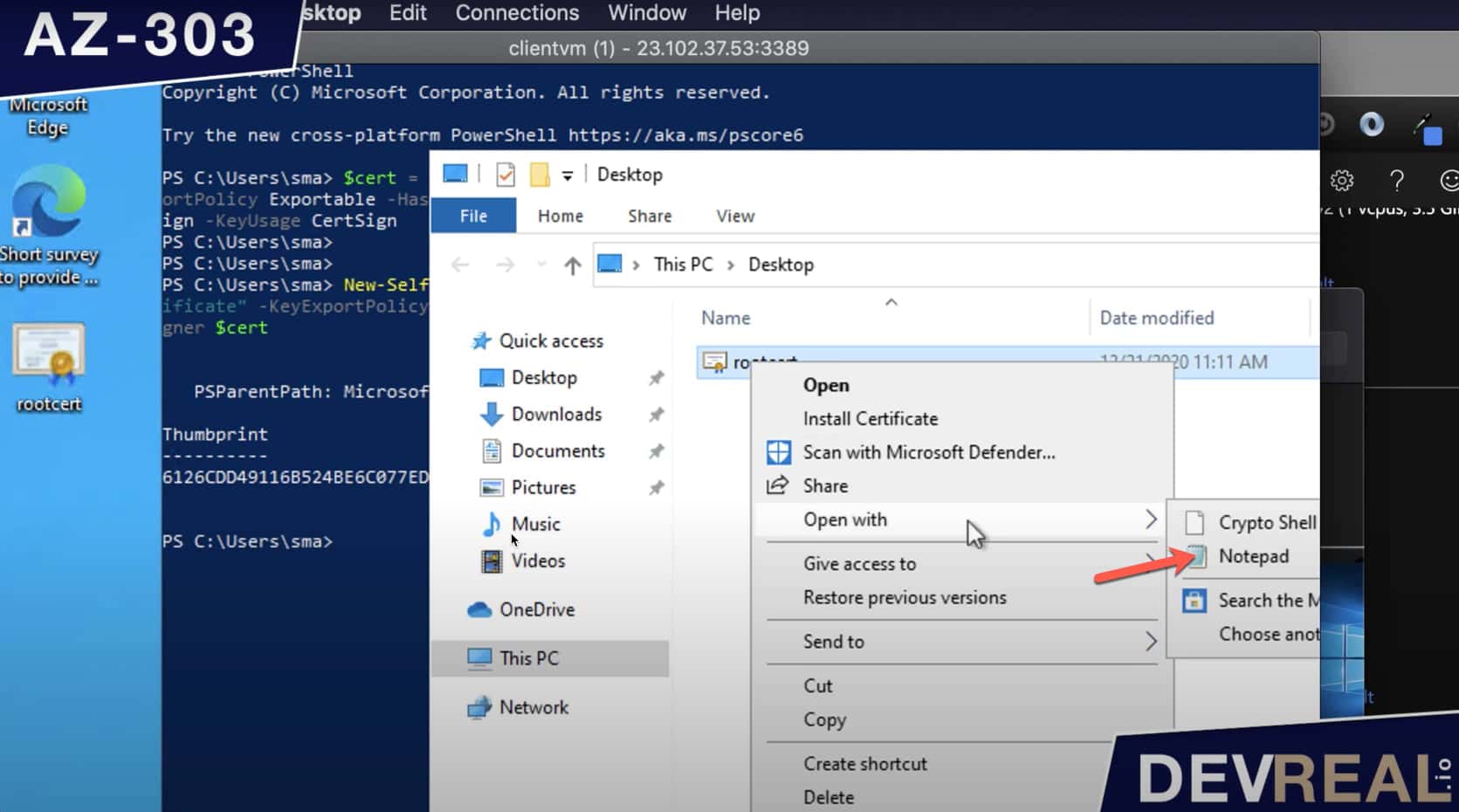 Read root certificate with Notepad
Read root certificate with Notepad
Select the content of the root certificate so you can copy it.
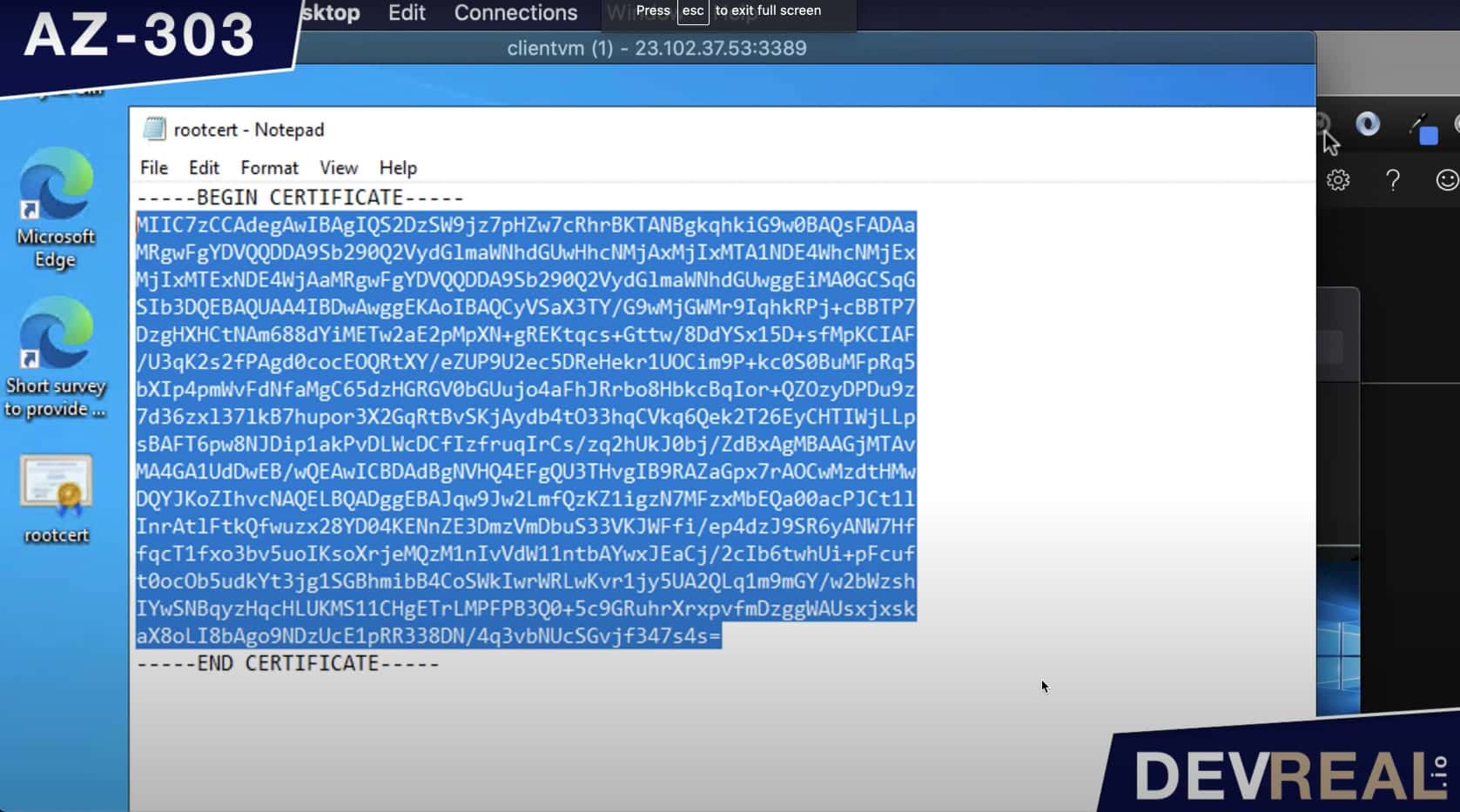 Copy content of root certificate
Copy content of root certificate
We head back in to the Azure portal and to the virtual network gateway. In the menu is the Point to Site Connection that we will open. The Point to Site Connection will represent your workstation. Set the address pool of it and then the tunnel type IKEv2 and SSTP (SSL). Then, we set the value of our root certificate as shown below.
Last, we download the VPN client on to our client workstation. I simply logged in to Azure from the client workstation and downloaded the VPN client from there.
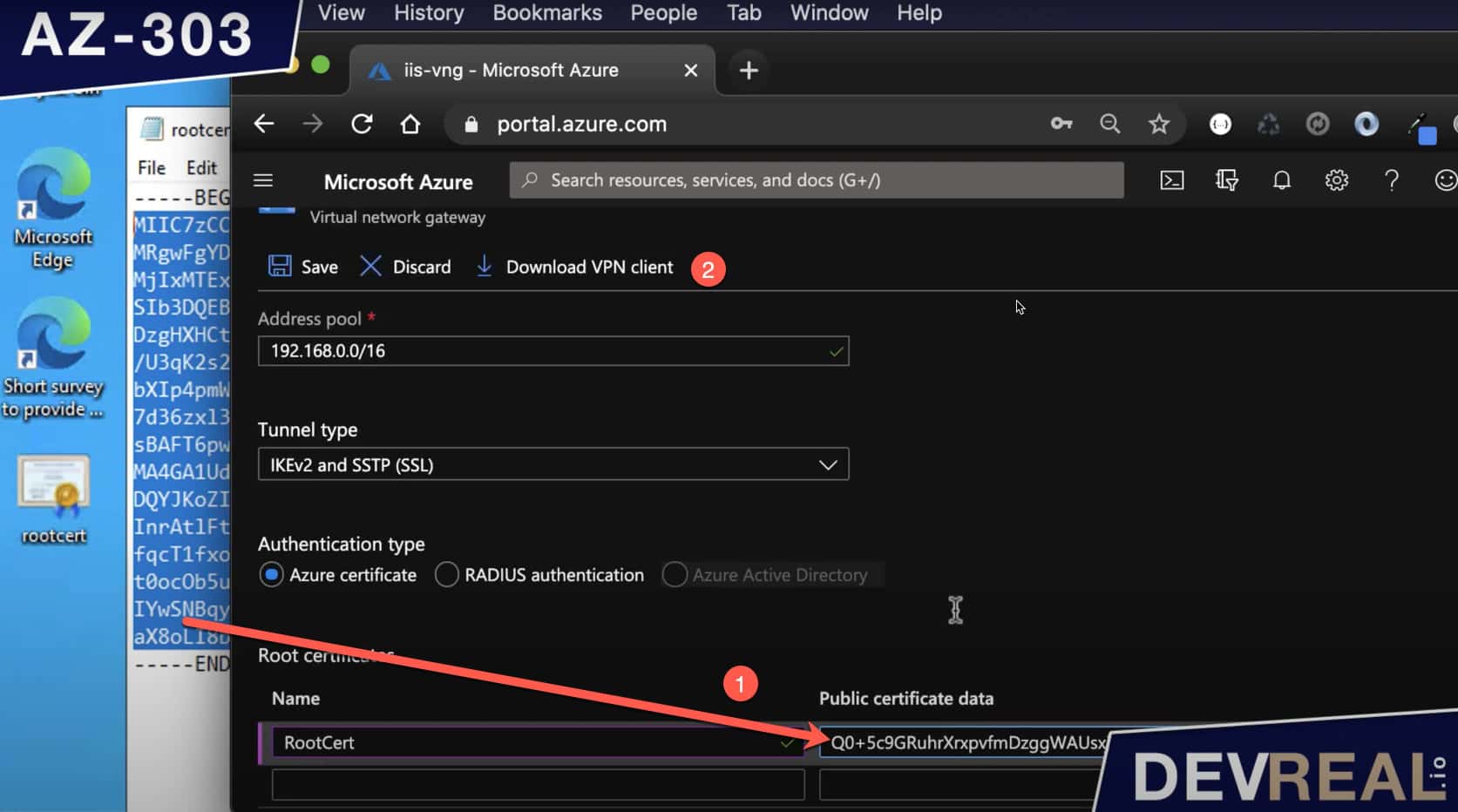 Configuring Point to Site Connection
Configuring Point to Site Connection
Extract the downloaded file and run it. It will install the VPN client on the workstation.
 Install VPN client
Install VPN client
Search for VPN settings and open it.
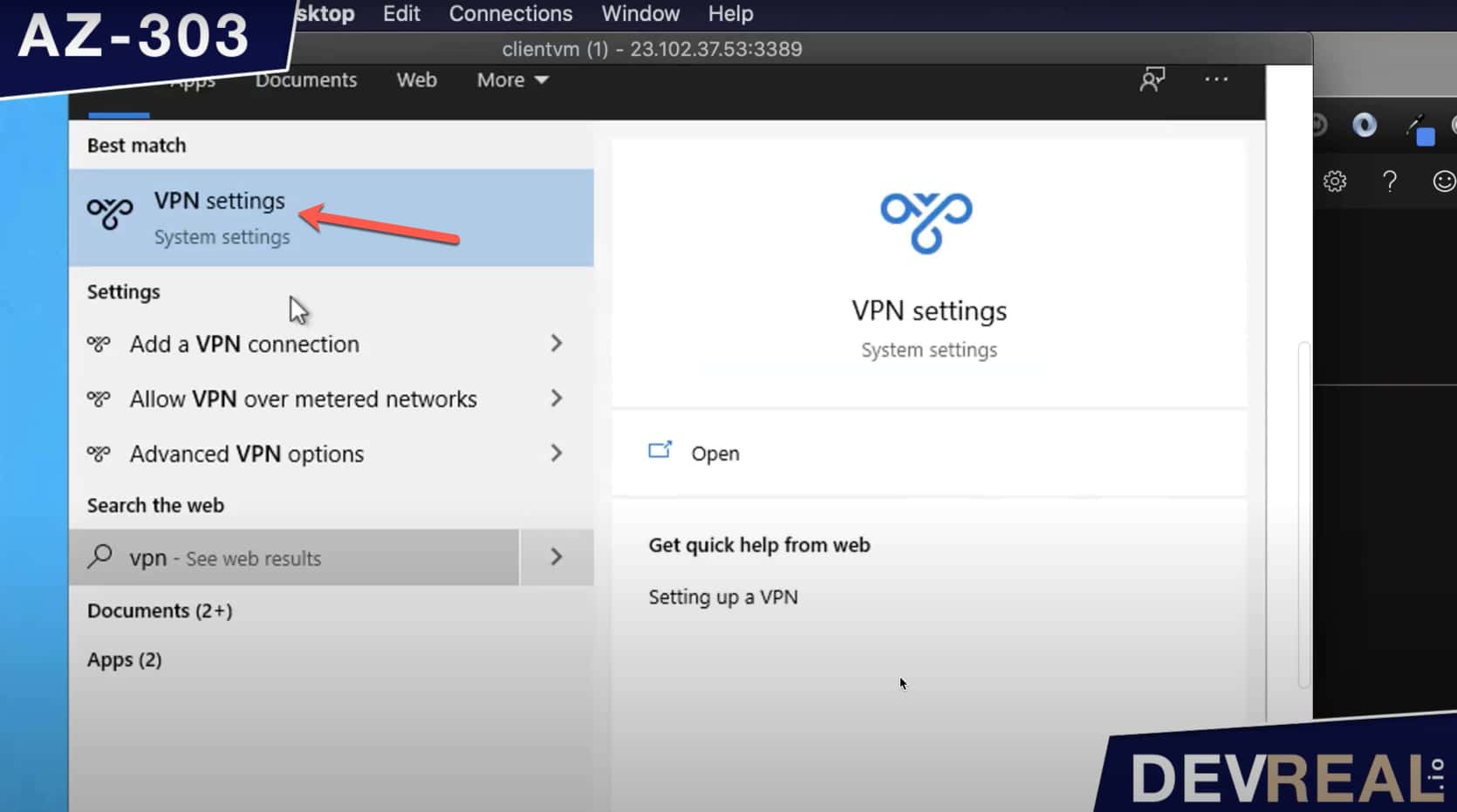 VPN settings
VPN settings
Now we can connect to the virtual network of the server.
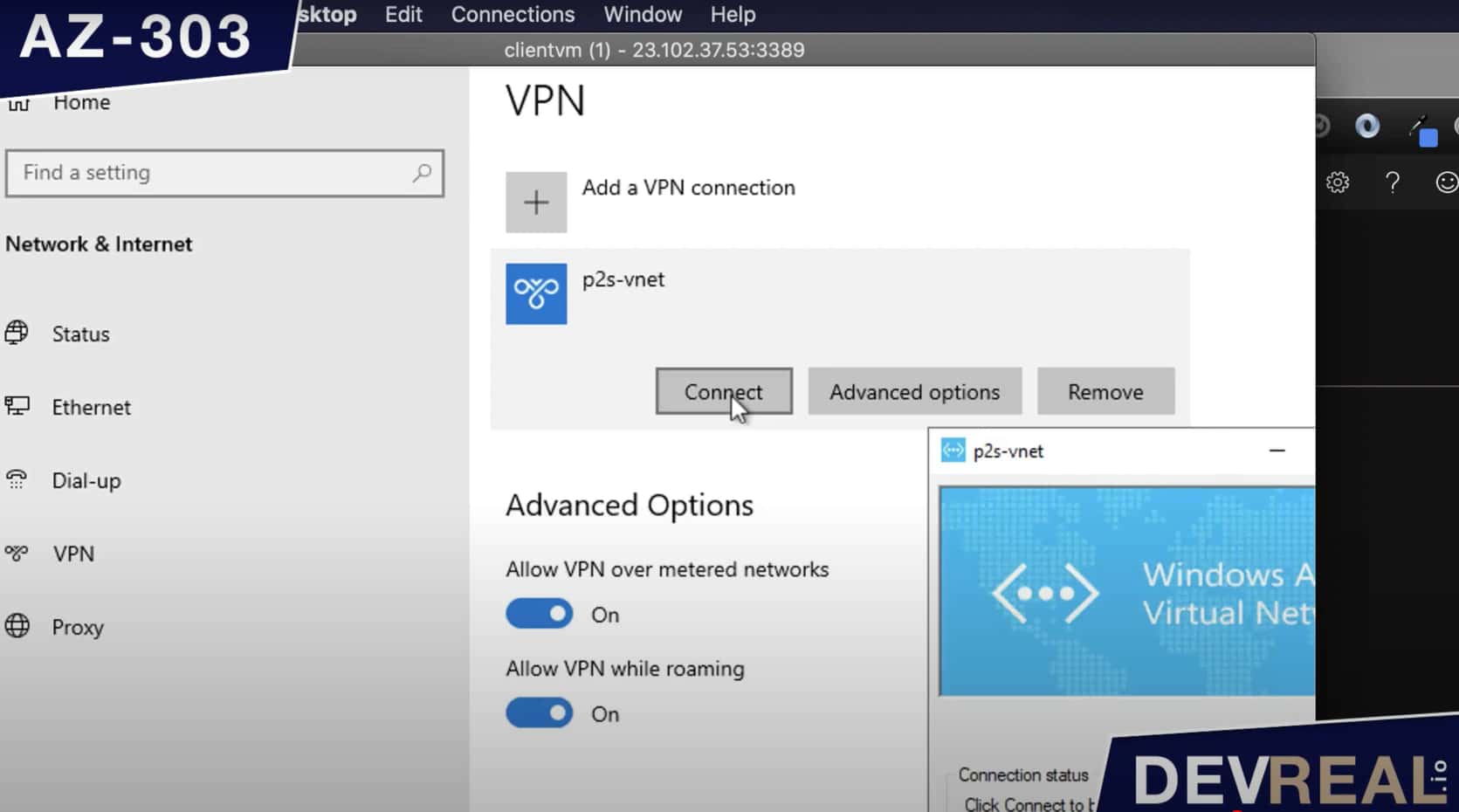 Connect to virtual network
Connect to virtual network
I checked the private IP address of the virtual machine running the IIS, 10.0.0.4. We open a browser, and vóila. We can access the IIS from our client workstation with a private IP address.
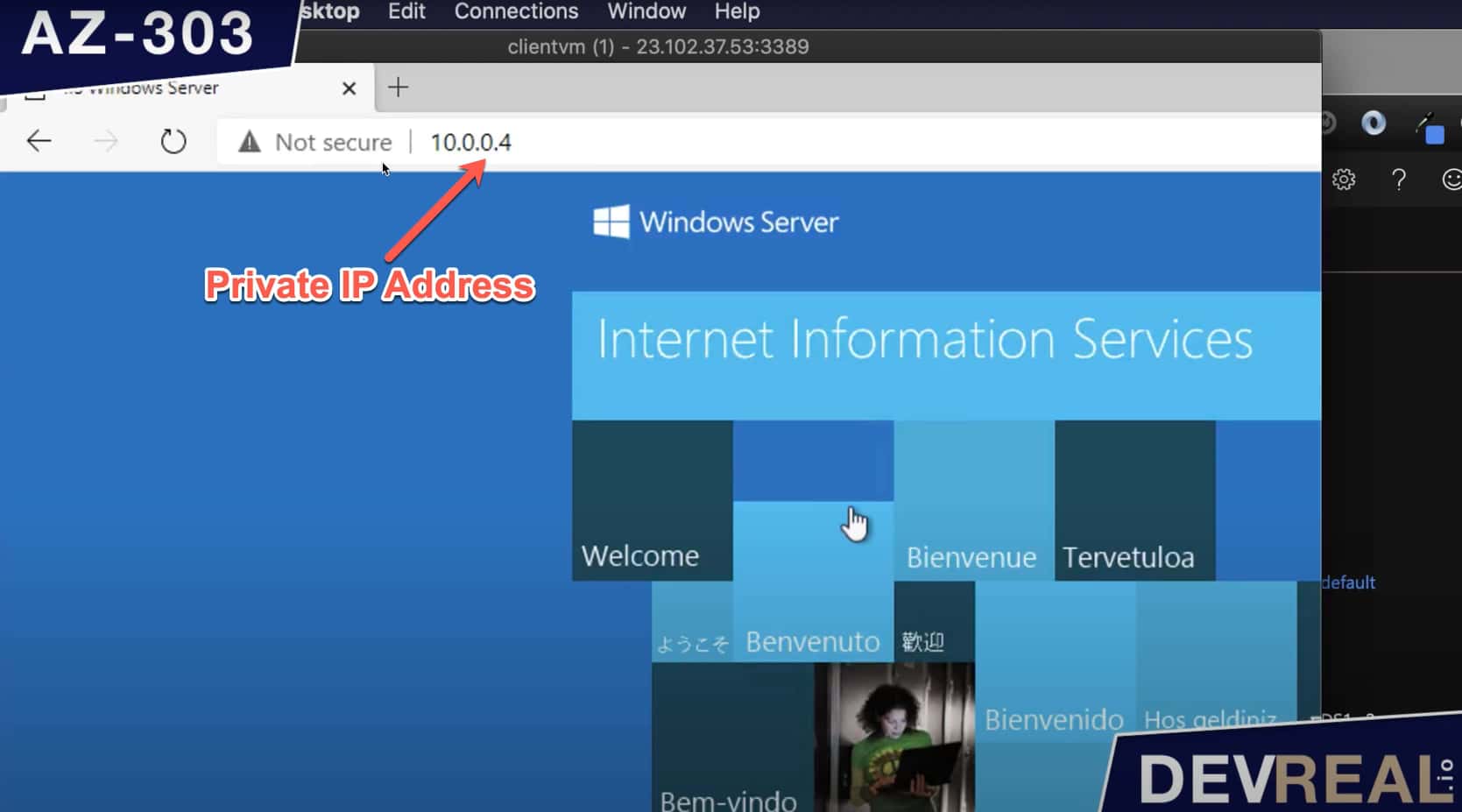 Access IIS with private IP address
Access IIS with private IP address
 Sven Malvik
Sven Malvik 








 Azure API Management at Norway
Azure API Management at Norway